My friend, I want to tell you this: This tutorial is written for you to solve such problems. I will walk you through the steps of developing a sample Java web project which utilizes the three frameworks Struts, Spring and Hibernate. The purpose of the application is to list all products from a MySQL database in a web page (JSP). Before going into the details, let’s review some key points first. I think these key points are very important as it helps us understand what is really going on with the integration at a high level. Why Integration of Struts, Spring and Hibernate? Struts is a web application framework, Spring is an enterprise application framework, and Hibernate is an ORM framework. Hibernate is working at the database layer, whereas both Struts and Spring can work at the web layer. Spring is more powerful than Struts and it can replace Struts. So if you are starting a new project with Spring and Hibernate, don’t use Struts! This kind of integration is only necessary for legacy projects which were built with Struts and now you have to upgrade them with Spring and Hibernate while still keeping Struts. Therefore, there are very few Struts-Spring-Hibernate applications in practice. How does the Integration of Struts, Spring and Hibernate work? In this kind of integration, Struts should intercept all requests coming to the application by working as a dispatcher filter. Spring should act as a dependency injection container which also manages Hibernate session and provides transaction management services. The interesting point is that Struts’ action classes are managed by Spring. Therefore, action mappings in Struts can refer to a Spring bean. This only can be done by using the Spring Plug-in provided by Struts.Back to the sample project we are going to develop in the next few minutes, I suggest you use the following technologies:
- Java 8
- Struts Framework 2.3.20
- Spring Framework 4.1.4.RELEASE
- Hibernate Framework 4.3.8.Final
- Tomcat 8.0
- Eclipse Luna (with Maven 3)
- MySQL 5.5
- Apache Commons DBCP
1. Setting Up Database
Execute the following MySQL script to create a database called productsdb with a table called product:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| CREATE DATABASE `productsdb`;CREATE TABLE `product` ( `product_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(128) NOT NULL, `description` varchar(512) NOT NULL, `price` float NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`product_id`)) |
2. Adding Maven Dependencies
First, declare properties for version numbers of Java, Struts, Spring, Hibernate and MySQL Connector library as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <properties> <java-version>1.8</java-version> <org.springframework-version>4.1.4.RELEASE</org.springframework-version> <org.strutsframework-version>2.3.20</org.strutsframework-version> <org.hibernateframework-version>4.3.8.Final</org.hibernateframework-version> <org.mysqlconnector-version>5.1.34</org.mysqlconnector-version></properties> |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework-version}</version></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework-version}</version></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> <version>${org.springframework-version}</version> <type>jar</type> <scope>compile</scope></dependency> |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId> <artifactId>struts2-core</artifactId> <version>${org.strutsframework-version}</version></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId> <artifactId>struts2-spring-plugin</artifactId> <version>${org.strutsframework-version}</version></dependency> |
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>${org.hibernateframework-version}</version></dependency> |
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-dbcp2</artifactId> <version>2.0</version></dependency> |
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>${org.mysqlconnector-version}</version></dependency> |
3. Coding and Mapping Model Class
Create a POJO class (Product.java) to model the product table in the database:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| /** * Copyright CodeJava.net To Present * All rights reserved. */package net.codejava.framework.model;public class Product { private long id; private String name; private String description; private float price; public long getId() { return id; } public void setId(long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; } public float getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(float price) { this.price = price; }} |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"><hibernate-mapping package="net.codejava.framework.model"> <class name="Product" table="PRODUCT"> <id name="id" column="PRODUCT_ID"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="name" /> <property name="description" /> <property name="price" /> </class> </hibernate-mapping> |
4. Coding DAO Classes
Because our application has only function - list all products - hence the following DAO interface (ProductDAO.java):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| /** * Copyright CodeJava.net To Present * All rights reserved. */package net.codejava.framework.dao;import java.util.List;import net.codejava.framework.model.Product;public interface ProductDAO { List<Product> list();} |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| /** * Copyright CodeJava.net To Present * All rights reserved. */package net.codejava.framework.dao;import java.util.List;import javax.transaction.Transactional;import org.hibernate.Criteria;import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;import net.codejava.framework.model.Product;public class ProductDAOImpl implements ProductDAO { private SessionFactory sessionFactory; public ProductDAOImpl(SessionFactory sessionFactory) { this.sessionFactory = sessionFactory; } @Override @Transactional public List<Product> list() { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List<Product> listProduct = (List<Product>) sessionFactory.getCurrentSession().createCriteria(Product.class) .setResultTransformer(Criteria.DISTINCT_ROOT_ENTITY) .list(); return listProduct; }} |
5. Coding Struts Action Class
Now, create a class that acts as a Struts action (ListProductAction.java) with the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| /** * Copyright CodeJava.net To Present * All rights reserved. */package net.codejava.framework.action;import java.util.List;import net.codejava.framework.dao.ProductDAO;import net.codejava.framework.model.Product;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;public class ListProductAction extends ActionSupport { private ProductDAO productDAO; private List<Product> listProduct; public void setProductDAO(ProductDAO productDAO) { this.productDAO = productDAO; } public String execute() { listProduct = productDAO.list(); return SUCCESS; } public List<Product> getListProduct() { return listProduct; }} |
6. Coding View Page
Create a JSP file called ProductList.jsp under the /WEB-INF/views directory (create the views directory first) with the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>Product List</title></head><body> <div align="center"> <table width="80%" border="1" style="border-collapse: collapse;"> <tr> <th>No</th> <th>Product Name</th> <th>Description</th> <th>Price</th> </tr> <s:iterator value="listProduct" status="stat"> <tr> <td><s:property value="#stat.count" /></td> <td><s:property value="name" /></td> <td><s:property value="description" /></td> <td><s:property value="price" /></td> </tr> </s:iterator> </table> </div></body></html> |
7. Configuring Web Deployment Descriptor (web.xml)
Configure Struts and Spring in the web.xml file as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1"> <display-name>Struts2Spring4Hibernate4XML</display-name> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <filter> <filter-name>DispatcherFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>DispatcherFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping></web-app> |
8. Configuring Hibernate framework
Create an XML file called hibernate.cfg.xml under the source directory with the following content:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?><!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"><hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <mapping resource="net/codejava/framework/model/Product.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory></hibernate-configuration> |
9. Configuring Struts framework
On the Struts side, create an XML file called struts.xml under the source folder and put the following code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"><struts> <package name="Struts2Spring4Hibernate4Demo" extends="struts-default"> <action name="listProduct" class="listProductActionBean"> <result name="success">/WEB-INF/views/ProductList.jsp</result> </action> </package></struts> |
Struts 2 for Beginners, 3rd Edition:
this book helps you come up to speed as quickly as possible with using
the Struts 2 framework. It is the latest book about Struts 2 to date.
10. Configuring Spring framework
On the Spring side, create an XML file called appContext.xml under the /WEB-INF/spring directory (create the spring directory first). Put the following XML code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <bean id="listProductActionBean" class="net.codejava.framework.action.ListProductAction"> <property name="productDAO" ref="productDAO" /> </bean> <bean id="productDAO" class="net.codejava.framework.dao.ProductDAOImpl"> <constructor-arg> <ref bean="sessionFactory" /> </constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml" /> </bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/productsdb" /> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="P@ssw0rd" /> </bean> <tx:annotation-driven /> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager"> <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" /> </bean></beans> |
Spring MVC: Beginner's Guide - This book helps beginners get started with the Spring MVC framework
instantly. It is a thorough introduction and reference on Spring MVC
framework.
- This book helps beginners get started with the Spring MVC framework
instantly. It is a thorough introduction and reference on Spring MVC
framework.
11. Final Project Structure
Hurray! We have done all the heavy stuff of Java code and XML configuration. Looking back, we have the following project structure: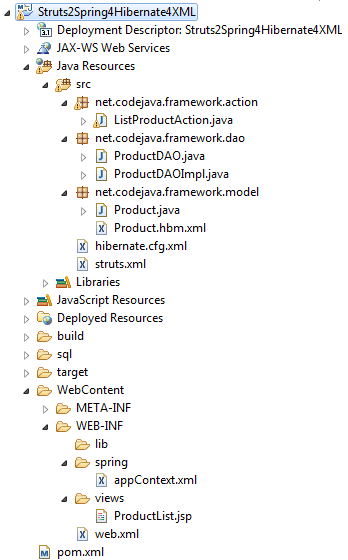 Refer to this in case you did something wrong.
Refer to this in case you did something wrong. 12. Testing the Application
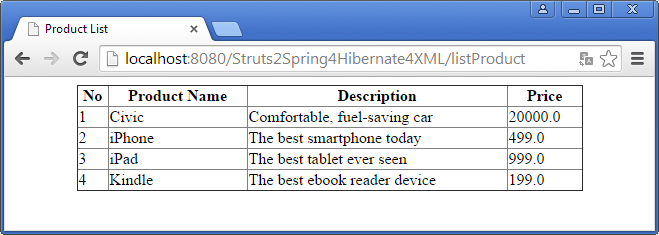
Now, it’s time to enjoy our hard work done so far. Deploy the application on Tomcat server and type the following URL into your browser to access the application: http://localhost:8080/Struts2Spring4Hibernate4XML/listProduct And here’s our sweet result: